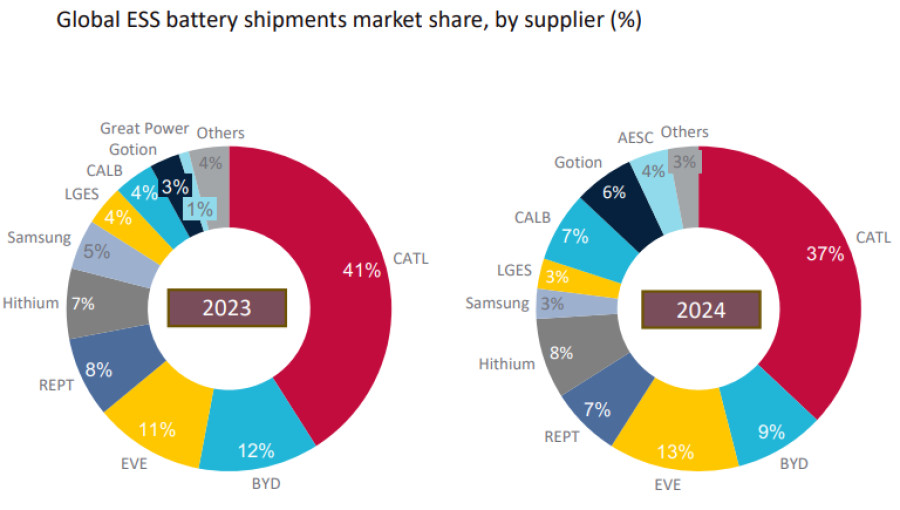
The global battery industry has seen an impressive expansion of nearly 83% over the past five years, significantly increasing energy storage deployment to over 300 GWh in 2024, according to a recent report by Intertek CEA. However, this growth is largely concentrated among a small number of suppliers, with five companies accounting for over 70% of the market. Notably, Chinese manufacturer CATL dominated the sector, holding a 37% share last year.
China’s changing policies are impacting the international market as well. The country’s recent anti-involution policy discourages low-cost competition by prohibiting the dumping of battery products at prices below production costs, leading to recent spikes in lithium prices. These measures aim to mitigate oversupply and competition among local lithium mines, with expectations of higher lithium carbonate prices going forward. Although prices have risen, they remain significantly lower than the previous year, with August 2023 prices being 80% cheaper than their August 2022 counterparts.
Aaron Marks, a consultant for Intertek CEA, highlighted that shifting national regulations could create price volatility, affecting global supply chains due to measures like export controls from China and bans from resource-rich countries such as Zimbabwe and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. He pointed out that while these changes may not create as much uncertainty as seen in the US, they still threaten to impact commodity and battery prices significantly. In the US, upcoming tariffs on batteries from China and other countries may shift buyer preferences towards suppliers that meet compliance requirements outlined in recent budget legislation.
With 83% tariffs on Chinese batteries taking effect in 2026, American buyers are expected to favor supply chains aligned with the foreign-entities-of-concern regulations. This situation could challenge Chinese suppliers, who may find it difficult to lower prices sufficiently to remain competitive while sustaining their operations. Conversely, if the demand for compliant modules outpaces the capacity of manufacturers in the US or ally nations, battery prices could increase, driving some companies to rely on Chinese production.
The evolving dynamics of the battery supply chain are prompting distinctions between compliant and non-compliant manufacturers, resulting in differences in cell design between Chinese and American or Korean producers. The report notes that the price gap between prismatic and pouch cells is widening, with pouch cells fetching approximately a 10% premium due to their energy density disadvantages. However, increased manufacturing capabilities could balance costs over time. Marks emphasized that the availability of compliant options will likely influence costs more significantly than the technical variances between cell types.